context.Context Code Reading
2023-05-12 Golang 并发编程 Go 源码分析 读代码
概述
context.Context 类型表示上下文信息,作用是在 API 通信、进程通信、函数调用之间传递超时时间、取消信号和其他数据值。
规则
使用 context.Context 时应遵循以下规则,以保证不同包之间的接口一致性,并启用静态分析工具来检查上下文的链路传播和可能产生的数据竞态。
- 不要将
context.Context嵌入结构体类型,应该明确地将其作为函数参数传递,并且应该是第一个参数,典型的命名为ctx - 不要传递一个值为
nil的context.Context, 即使函数内部并不使用这个参数。如果确定不了合适的context.Context类型,可以传递context.TODO类型 - 仅在 API 访问、进程通信之间使用
context.Value, 而不是将其作为可选参数传递给函数 context.Context可以在多个goroutine之间同时使用,同一个context.Context可以传递给不同的goroutine里面的函数
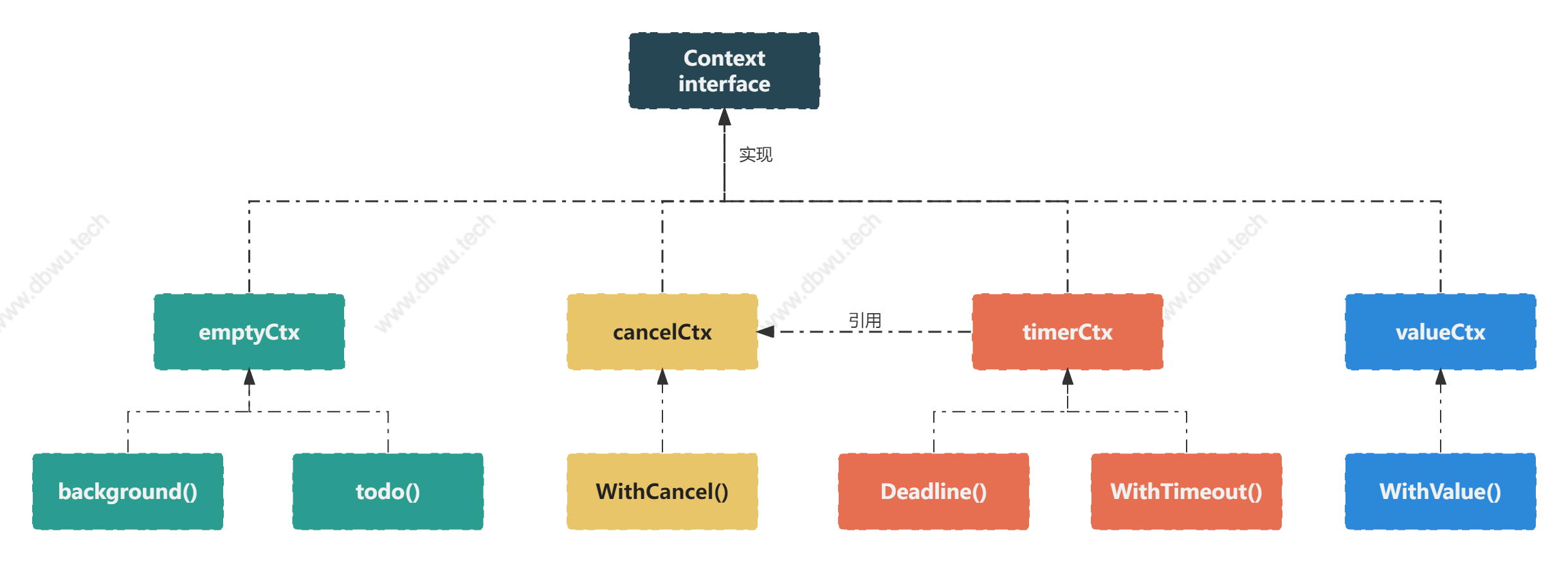
4 种类型
- emptyCtx: 所有
Context类型的基类型,使用context.TODO(),context.Background创建 - valueCtx: 可以在
Context中传递 1 个 K-V 键值对,它为 key 字段实现 Value 方法,并将调用委托给嵌入的Context - cancelCtx: 取消执行,当执行被取消时,子节点中实现
canceler接口的Context同样被取消 - timerCtx: 在
cancelCtx基础上封装一层,支持基于超时和定时器的cancelCtx
内部实现
我们来探究一下 context.Context 的内部实现,文件路径为 $GOROOT/src/context/context.go,笔者的 Go 版本为 go1.19 linux/amd64。
Context 接口
Context 接口用于在多个 API 之间传递超时时间、取消信号和其他数据值,接口的方法可以被多个 goroutine 并发调用。
type Context interface {
// Deadline 返回 Context 执行截止时间
// 如果没有设置截止时间, 返回 false
// 连续多次调用 Deadline 会返回相同的结果
Deadline() (deadline time.Time, ok bool)
// Done 返回一个只读 channel, 该 channel 在 Context 超时或被取消时关闭
// 如果 context 永远不会被取消,Done 返回 nil
// 连续多次调用 Done 会返回相同的结果
// Done channel 的关闭可能在 cancel 函数返回后异步执行
// 当 cancel 调用时,WithCancel 执行 Done 关闭
// 当 deadline 到期,WithDeadline 执行 Done 关闭
// 当 timeout 超时, WithTimeout 执行 Done 关闭
// Done 是在 select 语句中使用的
// 示例
// DoSomething 函数生成 values 并发送至 out,直到 DoSomething 返回一个错误或 ctx.Done 已经关闭
// func Stream(ctx context.Context, out chan<- Value) error {
// for {
// v, err := DoSomething(ctx)
// if err != nil {
// return err
// }
// select {
// case <-ctx.Done():
// return ctx.Err()
// case out <- v:
// }
// }
// }
//
// See https://blog.golang.org/pipelines for more examples of how to use
// a Done channel for cancellation.
Done() <-chan struct{}
// 如果 Done 还未关闭,返回 nil
// 如果 Done 已经关闭,根据下述情况返回具体的错误
// 如果 context 被取消,返回 Canceled
// 如果 deadline 到期,返回 DeadlineExceeded
// 如果返回一个非 nil 错误, 那么连续多次调用 Err 会返回同样的错误
Err() error
// Value 返回 Context 关联的 key 对应的值,如果没有值关联,返回 nil
// 连续多次使用相同的 key 参数,调用 Value, 会返回相同的结果
// key 标识 Context 的特定值
// 希望在 Context 中存储值的函数,通常会在全局变量中分配一个键
// 然后将该键作为参数传入 context.WithValue 和 Context.Value
// key 可以是任何支持 equality 的类型,应该将 key 定义为未导出类型,以避免冲突
// 示例
// // 包 user 定义了存储在 Context 中的 User 数据类型
// package user
//
// import "context"
//
// // User 是存储在 Context 中的值的类型
// type User struct {...}
//
// // key 是此包中定义的键的未导出类型
// // 这样可以防止与其他包中定义的 key 发生冲突
// type key int
//
// // userKey 是存储在 Context 中的 user.User 值的 key, 是未导出的
// // 调用方使用 user.NewContext 和 user.FromContext, 而不是直接使用 key
// var userKey key
//
// // NewContext 返回一个包含 User 类型值的 Context
// func NewContext(ctx context.Context, u *User) context.Context {
// return context.WithValue(ctx, userKey, u)
// }
//
// // FromContext 返回一个存储在 Context 中的 User 类型值
// func FromContext(ctx context.Context) (*User, bool) {
// u, ok := ctx.Value(userKey).(*User)
// return u, ok
// }
Value(key any) any
}
错误类型
Canceled 错误类型表示 Context 被取消执行,DeadlineExceeded 错误类型表示 Context 超时。
var Canceled = errors.New("context canceled")
var DeadlineExceeded error = deadlineExceededError{}
type deadlineExceededError struct{}
func (deadlineExceededError) Error() string { return "context deadline exceeded" }
emptyCtx 类型
emptyCtx 类型没有传递值,没有超时时间,也永远不会被调用,该类型实现了 Context 接口,但都是空实现。
需要注意的是,emptyCtx 不能定义为 struct{} 类型 (为了节省内存),因为该类型的变量必须有不同的地址 (空 struct{} 地址是唯一的)。
type emptyCtx int
func (*emptyCtx) Deadline() (deadline time.Time, ok bool) {
return
}
func (*emptyCtx) Done() <-chan struct{} {
return nil
}
func (*emptyCtx) Err() error {
return nil
}
func (*emptyCtx) Value(key any) any {
return nil
}
Background VS TODO 类型
Background, TODO 本质上都是 emptyCtx,只是定义了不同的别名用以区分,两者的语义分别如下:
- Background: 一般作为 Context 树的根结点
- TODO: 一般在无法确定应该使用哪种 Context 类型时,使用 TODO
var (
background = new(emptyCtx)
todo = new(emptyCtx)
)
func (e *emptyCtx) String() string {
switch e {
case background:
return "context.Background"
case todo:
return "context.TODO"
}
return "unknown empty Context"
}
// 语义:作为 Context 树的根结点
// Background 返回一个非 nil, 没有 values,没有 deadline,也永远不会被调用的 empty Context
// 典型使用场景有主函数,初始化,测试,以及作为顶级 Context 传入请求
func Background() Context {
return background
}
// 语义:不知道应该使用哪种 Context 类型时,使用 TODO
// TODO 返回一个非 nil 的 empty Context
// 当不清楚应该使用哪种 Context 类型,或者 Context 类型还不可用时(函数的调用栈存在不接收处理 Context 参数的情况),使用 context.TODO
func TODO() Context {
return todo
}
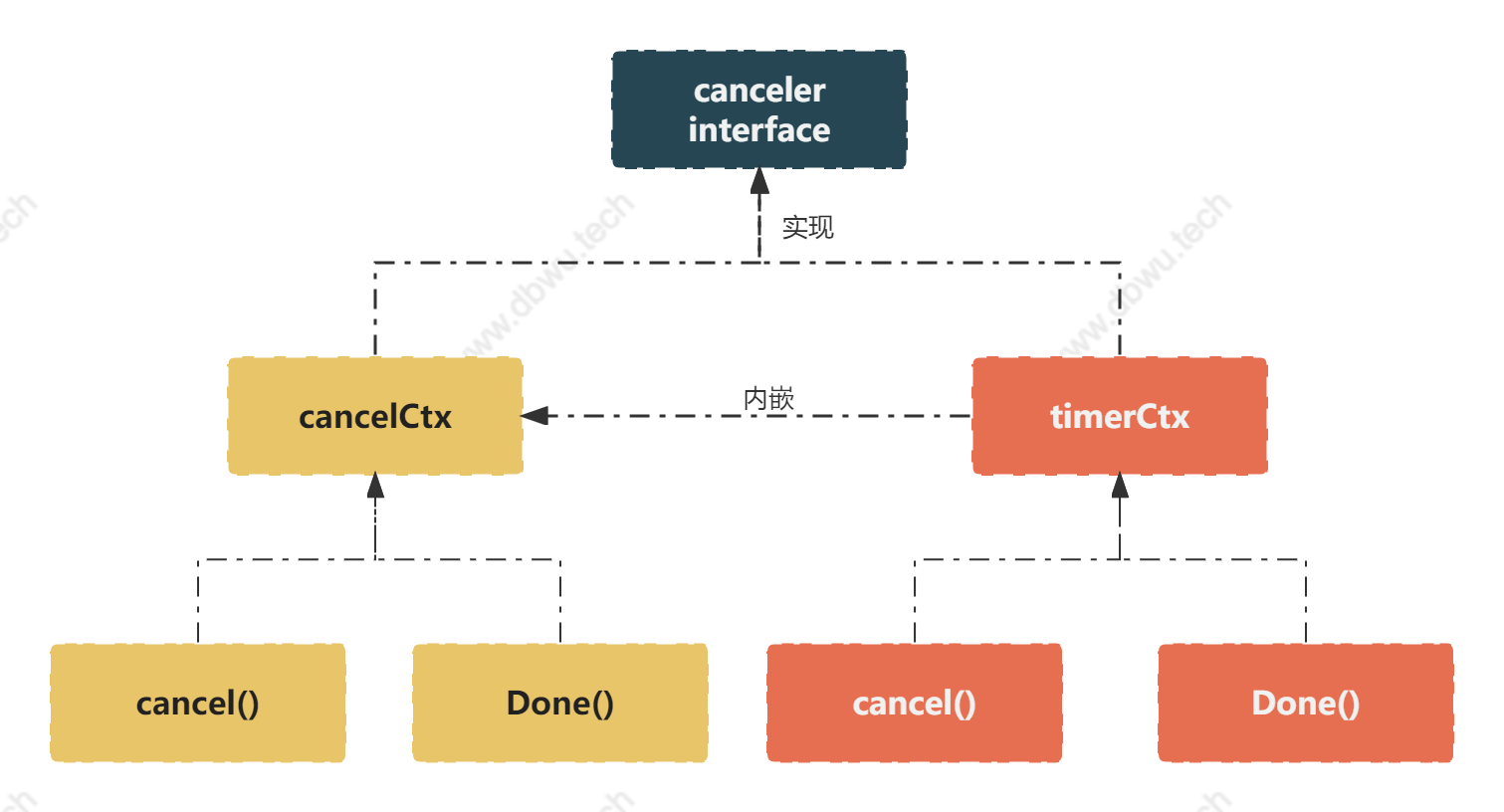
canceler 接口
// canceler 是一个可以被直接取消的 Context 类型
// *cancelCtx 和 *timerCtx 实现了这个接口
type canceler interface {
cancel(removeFromParent bool, err error)
Done() <-chan struct{}
}
Cancel 类型
// CancelFunc 通知一个操作放弃其执行(取消对应 Context)
// CancelFunc 不会等待执行停止
// CancelFunc 可以被多个 goroutine 并发调用
// CancelFunc 只有第一次调用有效,后续调用什么也不执行
type CancelFunc func()
// cancelCtx 实现取消操作,当它被取消时,同时取消所有实现了 canceler 接口的子节点
type cancelCtx struct {
Context
mu sync.Mutex // 保证下面三个字段的互斥访问
done atomic.Value // 懒惰式初始化,被第一个 cancel() 调用关闭
children map[canceler]struct{} // 被第一个 cancel() 重置为 nil
err error // 被第一个 cancel() 重置为 non-nil
}
// 复用了 Value 函数的回溯逻辑
// 从而在 Context 树回溯链中遍历时,可以找到给定 Context 的第一个祖先 cancelCtx 实例
func (c *cancelCtx) Value(key any) any {
// 特殊的 key: cancelCtxKey
if key == &cancelCtxKey {
return c
}
return value(c.Context, key)
}
func (c *cancelCtx) Done() <-chan struct{} {
d := c.done.Load()
if d != nil {
return d.(chan struct{})
}
c.mu.Lock()
defer c.mu.Unlock()
// double check
d = c.done.Load()
if d == nil {
// 惰式初始化
d = make(chan struct{})
c.done.Store(d)
}
return d.(chan struct{})
}
func (c *cancelCtx) Err() error {
c.mu.Lock()
err := c.err
c.mu.Unlock()
return err
}
// WithCancel 返回包装后的 Context 和用于取消该 Context 的函数 cancel
// 当 cancel 函数被调用,或者父 Context 被关闭时,返回的 Context 的 Done channel 会关闭
// 在 Context 涉及的上下文操作完成后,应该立即调用 cancel 函数,释放与 Context 关联的资源
func WithCancel(parent Context) (ctx Context, cancel CancelFunc) {
if parent == nil {
panic("cannot create context from nil parent")
}
c := newCancelCtx(parent)
propagateCancel(parent, &c)
return &c, func() { c.cancel(true, Canceled) }
}
// newCancelCtx 返回一个初始化后的 cancelCtx
func newCancelCtx(parent Context) cancelCtx {
return cancelCtx{Context: parent}
}
cancelCtx.cancel 方法
// 小技巧
// closedchan 表示一个可重用的已关闭 channel
var closedchan = make(chan struct{})
func init() {
// 初始化时关闭
close(closedchan)
}
// cancel 关闭 c.done channel, 取消 c 的所有子节点
// 如果 removeFromParent 为 true, 将 c 从其父节点中删除
func (c *cancelCtx) cancel(removeFromParent bool, err error) {
if err == nil {
// 需要给出取消的理由: Canceled or DeadlineExceeded
panic("context: internal error: missing cancel error")
}
c.mu.Lock()
if c.err != nil {
// 已经被其他 goroutine 取消
c.mu.Unlock()
return
}
// 记录错误
c.err = err
d, _ := c.done.Load().(chan struct{})
if d == nil {
// 惰式创建
c.done.Store(closedchan)
} else {
// 关闭 c.done
close(d)
}
// 级联取消
for child := range c.children {
// NOTE: 持有父节点锁的同时获取子节点的锁
child.cancel(false, err)
}
c.children = nil
c.mu.Unlock()
// 将 c 从其父节点中删除
if removeFromParent {
removeChild(c.Context, c)
}
}
Timer 类型
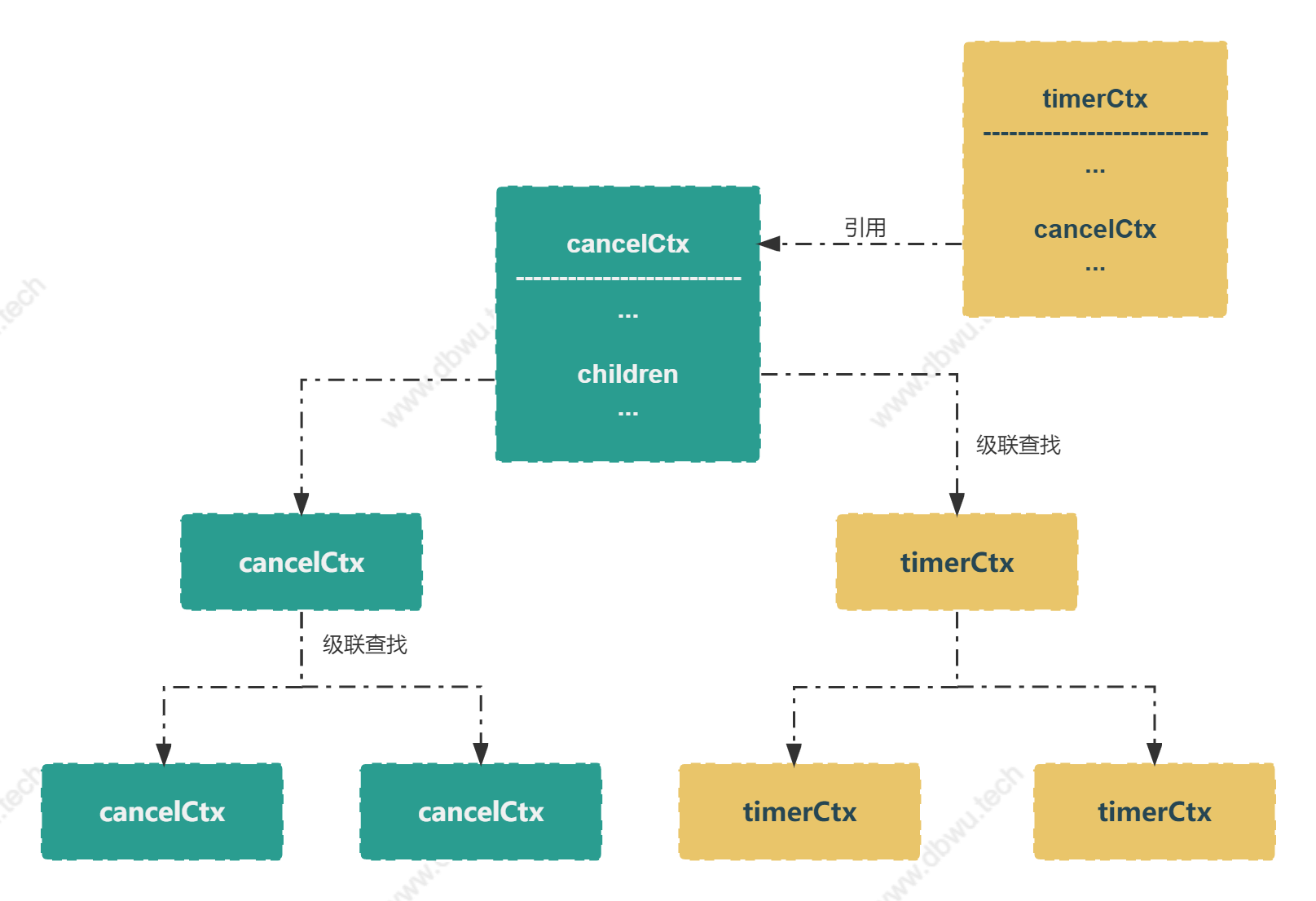
// timerCtx 类型包含一个定时器和一个超时时间
// 通过嵌入 cancelCtx 复用 Done() 方法和 Err() 方法
// 通过停止定时器然后委托给 cancelCtx.cancel() 方法
type timerCtx struct {
cancelCtx
timer *time.Timer
deadline time.Time
}
func (c *timerCtx) Deadline() (deadline time.Time, ok bool) {
return c.deadline, true
}
func (c *timerCtx) String() string {
...
}
// 在 Context 涉及的上下文操作完成后,应该立即调用 cancel 函数,释放与 Context 关联的资源
func WithTimeout(parent Context, timeout time.Duration) (Context, CancelFunc) {
return WithDeadline(parent, time.Now().Add(timeout))
}
timerCtx.cancel 方法
func (c *timerCtx) cancel(removeFromParent bool, err error) {
// 级联取消子树中所有 context
c.cancelCtx.cancel(false, err)
if removeFromParent {
// 从父节点中删除当前节点
removeChild(c.cancelCtx.Context, c)
}
c.mu.Lock()
if c.timer != nil {
// 关闭定时器 (避免 timer 泄漏)
c.timer.Stop()
c.timer = nil
}
c.mu.Unlock()
}
Value 类型
// valueCtx 包含 1 个 K-V 键值对,它为 key 字段实现 Value 方法,并将调用委托给嵌入的 Context
type valueCtx struct {
Context
key, val any
}
func (c *valueCtx) Value(key any) any {
if c.key == key {
return c.val
}
return value(c.Context, key)
}
// WithValue 将给定键值对包装进 Context 并返回
// key 必须具有可比性,不应该是 string 或其他内置类型,以避免调用方之间产生冲突,最好使用自定义类型作为 key
func WithValue(parent Context, key, val any) Context {
if parent == nil {
panic("cannot create context from nil parent")
}
if key == nil {
panic("nil key")
}
if !reflectlite.TypeOf(key).Comparable() {
panic("key is not comparable")
}
return &valueCtx{parent, key, val}
}
parentCancelCtx 方法
// parentCancelCtx 返回参数的第一个祖先 *cancelCtx
// 它通过查找 parent.Value(&cancelCtxKey), 来找到最内层的(回溯链中第一个) *cancelCtx
// 然后检查 parent.Done() 与 *cancelCtx 是否匹配
// 如果不匹配,说明 *cancelCtx 被包装在一个实现了 context.Context 接口的自定义 Context 中
func parentCancelCtx(parent Context) (*cancelCtx, bool) {
done := parent.Done()
if done == closedchan || done == nil {
return nil, false
}
p, ok := parent.Value(&cancelCtxKey).(*cancelCtx)
if !ok {
return nil, false
}
pdone, _ := p.done.Load().(chan struct{})
if pdone != done {
return nil, false
}
return p, true
}
propagateCancel 方法
// propagateCancel 实现节点编排: 当参数 (父节点) 取消时,同时取消其子节点
func propagateCancel(parent Context, child canceler) {
done := parent.Done()
if done == nil {
// 不可取消 (父节点是 emptyCtx 类型,或者自定义实现的 Context 类型)
return
}
select {
case <-done:
// 已经取消
child.cancel(false, parent.Err())
return
default:
}
if p, ok := parentCancelCtx(parent); ok {
// 找到一个 cancelCtx 实例
p.mu.Lock()
if p.err != nil {
// parent 已经取消
child.cancel(false, p.err)
} else {
if p.children == nil {
// 惰式创建
p.children = make(map[canceler]struct{})
}
p.children[child] = struct{}{}
}
p.mu.Unlock()
} else {
// 找到一个非 cancelCtx 实例
// 增加 goroutines 计数
atomic.AddInt32(&goroutines, +1)
go func() {
select {
case <-parent.Done():
child.cancel(false, parent.Err())
case <-child.Done():
}
}()
}
}
WithDeadline 方法
// WithDeadline 返回包装后的 Context 和用于取消该 Context 的函数 cancel
// 包装之后的 Context 的截止时间调整为参数 d
// 如果 parent 的截止时间已经早于参数 d, WithDeadline(parent, d) 在语义上就等于 parent
// 下面几种情况,不论哪种情况先发生,返回的 Context 的 Done channel 都会被关闭
// 1. 当返回的函数 cancel 被调用
// 2. 截止时间已到
// 3. 父节点的 Done channel 被关闭
// 在 Context 涉及的上下文操作完成后,应该立即调用 cancel 函数,释放与 Context 关联的资源
func WithDeadline(parent Context, d time.Time) (Context, CancelFunc) {
if parent == nil {
panic("cannot create context from nil parent")
}
if cur, ok := parent.Deadline(); ok && cur.Before(d) {
// parent 的截止时间更早
return WithCancel(parent)
}
// 包装一个新的 cancelCtx 实现部分接口
c := &timerCtx{
cancelCtx: newCancelCtx(parent),
deadline: d,
}
// 构建 Context 取消树,传入的是 c 而非 c.cancelCtx
propagateCancel(parent, c)
dur := time.Until(d)
if dur <= 0 {
// 截止时间设置的太接近,已经超时
c.cancel(true, DeadlineExceeded)
return c, func() { c.cancel(false, Canceled) }
}
// 设置超时取消
c.mu.Lock()
defer c.mu.Unlock()
if c.err == nil {
c.timer = time.AfterFunc(dur, func() {
c.cancel(true, DeadlineExceeded)
})
}
return c, func() { c.cancel(true, Canceled) }
}
小结
从应用层面来说,context.Context 主要用来在多个 goroutine 之间传递截止时间、取消信号,尤其是在多个层级函数调用栈中,
所以我们可以看到大多数第三方库提供的 API 中,第一个参数都是 context.Context, 此外,虽然 context.Context 也可以传递值,
但实际中很少使用这种方式,典型的场景比如传递 Request-ID, Token, Auth-Key 等。
从内部实现来说,context.Context 主要是基于 树形结构 + 互斥锁,这两者读者应该都比较熟悉,这里就不做赘述了。
这里列举一些内部实现中值得我们学习的代码技巧,比如 将具体错误公开为一个变量 的 DeadlineExceeded, 提供友好 API 的空实现 background, todo,
通过通道来表示一种变化标识符 的 closedchan。
扩展阅读
关于使用 Context.WithValue() 传递值的问题,在 《Concurrency in Go》 一书中,作者提到了几个观点:
- 值可以跨 API 访问
- 值应该是不可变的
- 值应该是简单的数据类型
- 值应该是具体数据,而非某个类型或方法
- 不同的值不会影响到后续的链路逻辑
该书作者还给出了几种常见的 传递值,并与上面的 5 点要求进行了对比:
| 值类型/要求 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Request ID | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| User ID | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| URL | √ | √ | |||
| API Server Connection | |||||
| Auth Token | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| Request Token | √ | √ | √ |