容器中如何正确配置 GOMAXPROCS ?
2023-04-30 Golang Docker Go 源码分析 读代码
前言
前两天看了一篇文章 GOMAXPROCS 与容器的相处之道,里面提到了 Go 标准库中 runtime.GOMAXPROCS 方法的问题:
因为系统调用
sched_getaffinity并不感知它对进程的限制,所以运行在 Kubernetes 中的 Go 程序的运行时始终会认为自己可以使用宿主机上的所有 CPU,进而创建了相同数量的 P (处理器), 而当 GOMAXPROCS 被手动地设置为限制后的值后,CPU 密集型场景的性能就得到了很大提高。
Go 标准库在应用层面并没有给出任何解决方案,Uber 公司的技术团队针对这个问题开发并开源了组件 automaxprocs,
对于需要严格限制 P 数量 的业务场景,可以使用该组件在运行时根据容器中 CGroups 的配置动态修改 GOMAXPROCS,避免资源的不合理使用。
内部实现
我们一起探究下 automaxprocs 组件的内部代码实现,笔者选择的版本为 v1.5.1。
备注: 如果读者对 CGroups 概念尚不清晰,建议先阅读一下这篇文章 Docker 基础支撑技术概览。
示例程序
package main
import (
_ "go.uber.org/automaxprocs"
"fmt"
"runtime"
"time"
)
func main() {
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
go func() {
time.Sleep(time.Millisecond)
}()
}
// 输出 CPU Core 的数量
// 输出处理器 P 的数量
fmt.Printf("CPU number = %d, P number = %d\n", runtime.NumCPU(), runtime.GOMAXPROCS(-1))
time.Sleep(time.Second)
}
宿主机运行
$ go run main.go
# 输出如下
CPU number = 8, P number = 8
笔者的宿主机 CPU 配置为 8 Core,通过输出的信息可以看到处理器的数量并没有被限制。
容器运行
接下来构建一个配置为 –cpus=2 的容器运行上面的代码:
$ go run main.go
# 输出如下
CPU number = 2, P number = 2
通过输出的信息可以看到处理器的数量已经被限制。
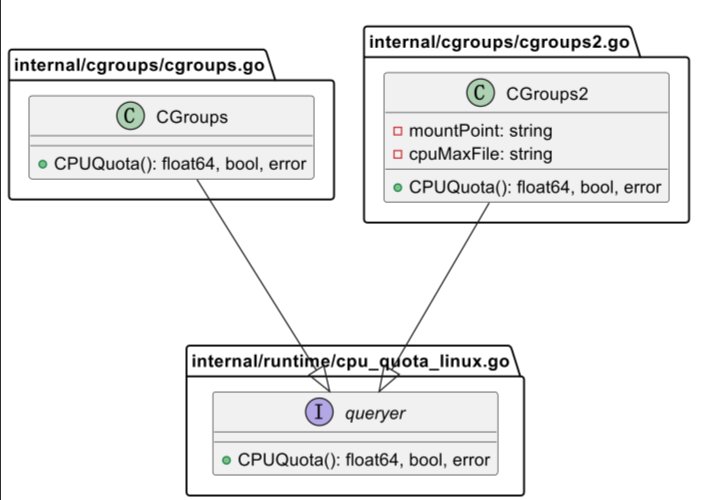
接口
automaxprocs 组件同时兼容 CGroups 和 CGroups2, 通过 queryer 接口来抽象隔离具体的版本实现。
type queryer interface {
CPUQuota() (float64, bool, error)
}
var (
_newCgroups2 = cg.NewCGroups2ForCurrentProcess
_newCgroups = cg.NewCGroupsForCurrentProcess
)
CGroups2 是 CGroups 的升级版本,提供了统一的控制系统并增强了资源管理能力,详情可以参考这篇文章 About cgroup v2。
# 确认当前系统的 CGroups 版本
$ stat -fc %T /sys/fs/cgroup/
# CGroups 输出 tmpfs
# CGroups2 输出 cgroup2fs
笔者使用的 Ubuntu 版本为 tmpfs, 所以下面的代码研究以 CGroups 实现为主。
初始化函数
automaxprocs 包内注册了 init 方法,会被其被引用时自动调用。
package automaxprocs
func init() {
maxprocs.Set(maxprocs.Logger(log.Printf))
}
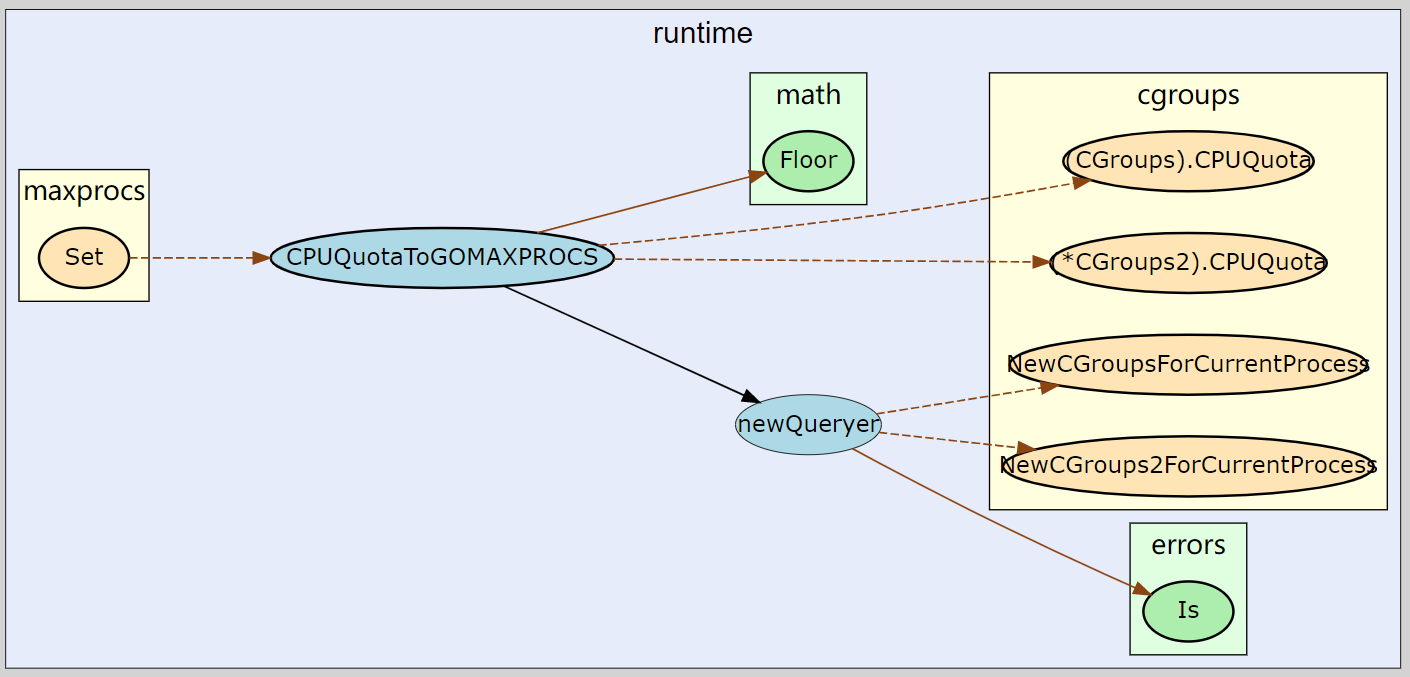
Set 函数
Set 函数是功能实现的核心代码,它会自动匹配 Linux 容器中的 CPU 资源配额并更改 GOMAXPROCS,对于非 Linux 系统或者没有配置 CPU 资源配置的 Linux 系统,
该方法什么也不做,最后方法返回一个 error 和一个 undo 函数 (用来撤销针对 GOMAXPROCS 所作的修改)。
题外话: 这个返回的 undo 函数小技巧值得学习 (设计模式之状态模式)。
func Set(opts ...Option) (func(), error) {
cfg := &config{
// 用来获取 CPU 资源配额的方法
procs: iruntime.CPUQuotaToGOMAXPROCS,
// GOMAXPROCS 最小值为 1
minGOMAXPROCS: 1,
}
...
// 默认的 undo 函数
undoNoop := func() {
}
if max, exists := os.LookupEnv(_maxProcsKey); exists {
// 如果已经设置了 GOMAXPROCS 环境变量,就以环境变量为准
// 不做任何操作,直接返回
return undoNoop, nil
}
// 获取 CPU 资源配额
maxProcs, status, err := cfg.procs(cfg.minGOMAXPROCS)
...
// 未设置 CPU 资源配额,直接返回
if status == iruntime.CPUQuotaUndefined {
return undoNoop, nil
}
// 获取当前 GOMAXPROCS 值
prev := runtime.GOMAXPROCS(0)
// undo 函数更新,恢复到未修改前的 GOMAXPROCS 值
undo := func() {
runtime.GOMAXPROCS(prev)
}
...
runtime.GOMAXPROCS(maxProcs)
return undo, nil
}
CPUQuotaToGOMAXPROCS 函数
CPUQuotaToGOMAXPROCS 函数用于获取 Linux 容器中的 CPU 资源配额,具体的实现是由 newQueryer 函数完成的。
func CPUQuotaToGOMAXPROCS(minValue int) (int, CPUQuotaStatus, error) {
cgroups, err := newQueryer()
...
quota, defined, err := cgroups.CPUQuota()
...
maxProcs := int(math.Floor(quota))
// 如果 CPU 配额比配置的最小值还要小
// 就以配置的最小值为准
if minValue > 0 && maxProcs < minValue {
return minValue, CPUQuotaMinUsed, nil
}
return maxProcs, CPUQuotaUsed, nil
}
newQueryer 函数
newQueryer 函数并没有判断当前系统的 CGroups 版本,而是优先获取 CGroups2 的配置,如果获取不到,再获取 CGroups 的配置。
func newQueryer() (queryer, error) {
// 优先获取 CGroups2 配置
cgroups, err := _newCgroups2()
if err == nil {
return cgroups, nil
}
if errors.Is(err, cg.ErrNotV2) {
// 其次获取 CGroups 配置
return _newCgroups()
}
return nil, err
}
NewCGroupsForCurrentProcess 函数用来获取 CGroups 版本的配置,具体的实现是 NewCGroups 函数完成的。
func NewCGroupsForCurrentProcess() (CGroups, error) {
return NewCGroups(_procPathMountInfo, _procPathCGroup)
}
NewCGroups 函数通过读取 /proc/self/mountinfo 和 /proc/self/cgroup 文件获取配置,最后包装成 CGroups 接口对象返回。
// CGroups 接口对象
type CGroups map[string]*CGroup
func NewCGroups(procPathMountInfo, procPathCGroup string) (CGroups, error) {
...
}
CPUQuota 方法
最后,我们看来看下 CGroups 版本的 CPU 资源配额是如何计算出来的,该功能由 CPUQuota 方法完成。
该方法首先获取 cpu.cfs_quota_us 和 cpu.cfs_period_us 两个字段:
cpu.cfs_quota_us: CPU 周期内最多可使用的时间 cpu.cfs_period_us: CPU 周期时间
例如:如果 cpu.cfs_quota_us 是 cpu.cfs_period_us 的 4 倍,表示允许容器使用 4 个 CPU Core。
如果上述两个字段任意一个未设置,方法返回 -1,表示不限制对 CPU 资源的使用,如果两个字段都设置了,使用下面的公式返回资源配额:
cpu.cfs_quota_us / cpu.cfs_period_us
func (cg CGroups) CPUQuota() (float64, bool, error) {
...
cfsQuotaUs, err := cpuCGroup.readInt(_cgroupCPUCFSQuotaUsParam)
...
cfsPeriodUs, err := cpuCGroup.readInt(_cgroupCPUCFSPeriodUsParam)
...
return float64(cfsQuotaUs) / float64(cfsPeriodUs), true, nil
}
小结
uber-go/automaxprocs 组件通过读取运行时环境中的 CGroups 相关配置文件,完成动态修改 GOMAXPROCS 功能。
Reference
- uber-go/automaxprocs
- Docker 基础支撑技术概览
- GMP 调度器
- GOMAXPROCS 与容器的相处之道
- About cgroup v2
- CFS Bandwidth Control